Introduction
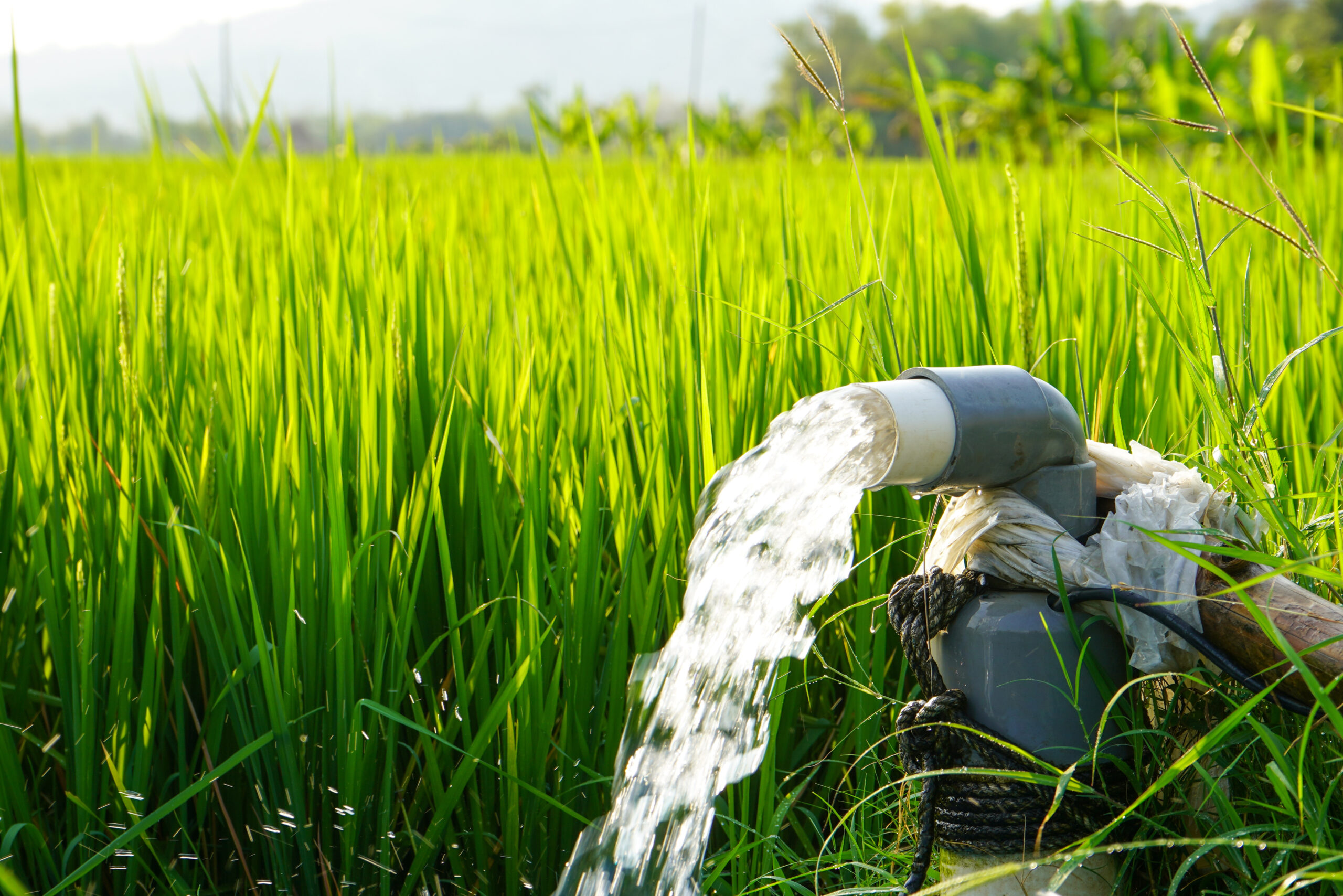
A water pump is a machine that transports or pressurizes liquid, applied to various water treatment systems. Affecting the water use and related activities of many people. An understanding of water pumps can help you solve your problems.
How Does a Water Pump Work?
You might want to know how a water pump works. How can such a relatively small machine continuously output water?
Basic Process
The basic principle of water pump operation is that the impeller of the water pump rotates at high speed, driven by a motor, transferring mechanical energy to the water, giving it kinetic and pressure energy to achieve transportation.
Principle
When the water pump starts, the impeller rotates at high speed, and water is pushed into the volute and is discharged. This causes a vacuum at the inlet, and the water outside will be sucked under pressure. It circulates continuously to deliver water stably.
Difference
There are also some principal differences between different types of water pumps. Such as
Centrifugal pumps depend on centrifugal force to work, while positive displacement pumps operate through changes in volume.
Main Components of a Water Pump
The stable operation of the water pump is the result of the cooperation of various components. Especially the main accessories play an important role.
Motor or engine: Convert power into kinetic energy to drive the water pump.
Impeller: Rotates at high speed, driven by the motor, giving the liquid pressure and kinetic energy. Common materials include PPO, copper, stainless steel, and aluminum, etc.
Pump casing/housing: Protect the internal parts of the water pump and guide the delivery of water flow.
Shaft: Transfer the kinetic energy brought by the rotation of the rotor
Seal: Prevents liquid leakage along the shaft and prevents air from entering the pump
Inlet and outlet: Responsible for the suction and discharging of liquid, and connecting pipes to transport liquids
Pressure switch or intelligent controller: Automatically controls the start and stop of the pump by sensing pressure to achieve a constant water supply and save energy
Types of Water Pumps
Water pumps can be divided into a wide range of types, from slightly different working principles to their unique characteristics. Their functionality enables them to meet a wide variety of needs and water treatment systems.
Centrifugal Pumps
Centrifugal pumps have a simpler structure, are smaller and lighter, making them more suitable for small-scale water use, such as home use and garden irrigation.
Submersible Pumps
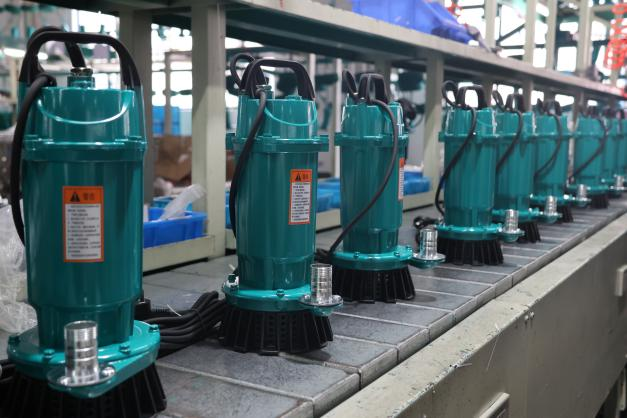
Submersible pumps can operate completely submerged in liquid. Their one-piece design and corrosion-resistant properties make them suitable for deep wells, drilling, or wastewater treatment.
Jet Pumps
Water is drawn in by generating negative pressure through the nozzle. And it has a strong self-priming ability and can draw water from deep wells.
Booster Pumps
Specifically designed to increase water pressure, these pumps provide a stable water flow and are ideal for water supply in high-rise buildings.
Sewage Pumps
The impeller, with its high wear resistance, effectively discharges wastewater containing solids or impurities, thus treating various types of sewage and wastewater.
Self-Priming Pumps
A self-priming pump is a type of water pump that requires only one water filling before startup to draw water automatically. It starts quickly and is suitable for frequent start-stop or mobile applications.
Intelligent Pumps / Variable Frequency Pumps
Intelligent pump automatically adjusts the motor speed according to water demand to achieve a constant pressure water supply. It can also automatically start and stop, making it energy-efficient.
Applications by Type
The variety of water pumps makes them widely used in various fields. Below are some of the main industry sectors and their specific applications.
Domestic use
Household Water Supply: Pressurized water supply, well water extraction.
Garden Irrigation: Sprinkler systems, drip irrigation systems.
Household Drainage: Basement drainage, sewage lifting.
Swimming Pool Circulation and Filtration: Swimming pool circulation pumps, SPA pumps.
Agricultural use
Farmland Irrigation: Sprinkler irrigation, drip irrigation, greenhouse irrigation.
Deep Well Pumping: Agricultural deep well submersible pumps.
Livestock Water Supply: Livestock farm water supply, drinking water systems.
Fertilizer Sprinkler Irrigation System Pumps:
Industrial use
Industrial Cooling Water Circulation: Machine tool cooling, industrial equipment cooling.
Factory Production Water: Process flow pumps, chemical delivery pumps.
Chemical and Petrochemical Industry: Corrosion-resistant pumps, metering pumps.
High-Pressure Cleaning Systems: High-Pressure plunger pumps.
Sewage and Drainage Treatment
Urban Water Supply Systems: Large booster pumps, centrifugal pumps.
Sewage and Wastewater Treatment: Sewage pumps, mud pumps, lift pump stations.
Stormwater Drainage Systems: Flood control and drainage pump stations.
Green and Renewable Applications
Solar Water Pumps: Off-grid agricultural irrigation, pastoral water supply.
Storage Tank Circulation and Transportation Systems.
Energy-saving variable frequency water supply system: Intelligent variable frequency pump.
Marine Applications
Bilge pump: Bilge pumps are used to remove water accumulated in the bilge of ships
Seawater circulation pump: Used to circulate seawater, often in cooling systems.
Desalination system pump: Specialized water pumps used in seawater desalination are responsible for different processes, such as pressurization and transportation.
Municipal and Public Works
Urban Water Supply System: Transporting water to the city water supply pipes and pressurizing the water supply to high-rise buildings.
Sewage and Wastewater Treatment: Able to collect, transport, and treat various types of sewage and wastewater.
Stormwater Drainage System: Drain stagnant rainwater, prevent flood disasters, and ensure the operation of urban drainage systems
How to Choose the Right Water Pump
A brief overview of the factors involved in selecting the right water pump is crucial, as these factors not only significantly impact the purchase process but are also key indicators of pump quality.
Flow rate and head
Flow rate and head determine how much water a water pump can deliver and how high and far it can carry the water. You can choose the water pump with the correct delivery capacity according to your needs.
Water source type
Where do you want to draw water or liquid—from a well, a river, or a sewage pit? Depending on the water source, you can choose a suitable water pump; for example, a deep well pump can be used for a well.
Power supply (voltage, frequency)
Power supply is also a key factor; choose a water pump that matches the local voltage and power frequency. If you prefer solar power, you can also choose a solar water pump.
Installation condition
Knowing clearly what water pumps are suitable for the installation environment will help you locate the water pump type quickly. Submersible pumps are specifically designed for situations where the pump is immersed in liquid, while surface pumps are used on the shore.
Material and durability
Choose a material that is compatible with the liquid. Like, in corrosive liquids, corresponding corrosion-resistant materials are required, such as stainless steel and aluminum, etc.
Conclusion
The water pumps play a key role in the water supply system. Choosing the right water pump can offer long-term stable operation, extend the service life, and reduce maintenance costs. At the same time, it improves pump efficiency, letting users have fewer worries.
For reliable and efficient water pumping solutions, trust Hungerät. With years of experience in water pumps, we have helped many customers find the most suitable water pumps and provide high-quality water pumps.
FAQ
Q: What are the main types of water pumps?
A: Normal types include centrifugal pumps, submersible pumps,self-priming pumps, booster pumps, and sewage pumps. Different types that equip their own unique functions and advantages suitable for various scenes, you can choose pumps depending on your requirements.
Q: What’s the difference between a centrifugal pump and a submersible pump?
A: Centrifugal is usually installed on the surface to boost shallow water extraction. Submersible pumps are needed to immerse in liquid, which is more suited to deep wells and wastewater treatment environments.
Q: What materials are water pumps made of?
A: The materials used to manufacture water pumps are typically made of copper, stainless steel, aluminum, and PPO, etc. Its wide range of material choices allows the water pump to operate normally in various water qualities.
Q: What’s the difference between a water pump and a booster pump?
A: A booster pump is a type of water pump specifically designed to increase water pressure, resulting in a more stable water flow and faster water output. It is suitable for water supply in high-rise buildings. Water pumps are a broad, general concept that includes many types and serves many functions and applications.
Q: How do I know which pump is right for me?
A: Determine your purpose and usage environment, choose your required head and flow, and consider the type of liquid and power supply condition. If you’re still struggling to choose a water pump, you can consult professional manufacturers such as Hungerät to get the most suitable suggestions.