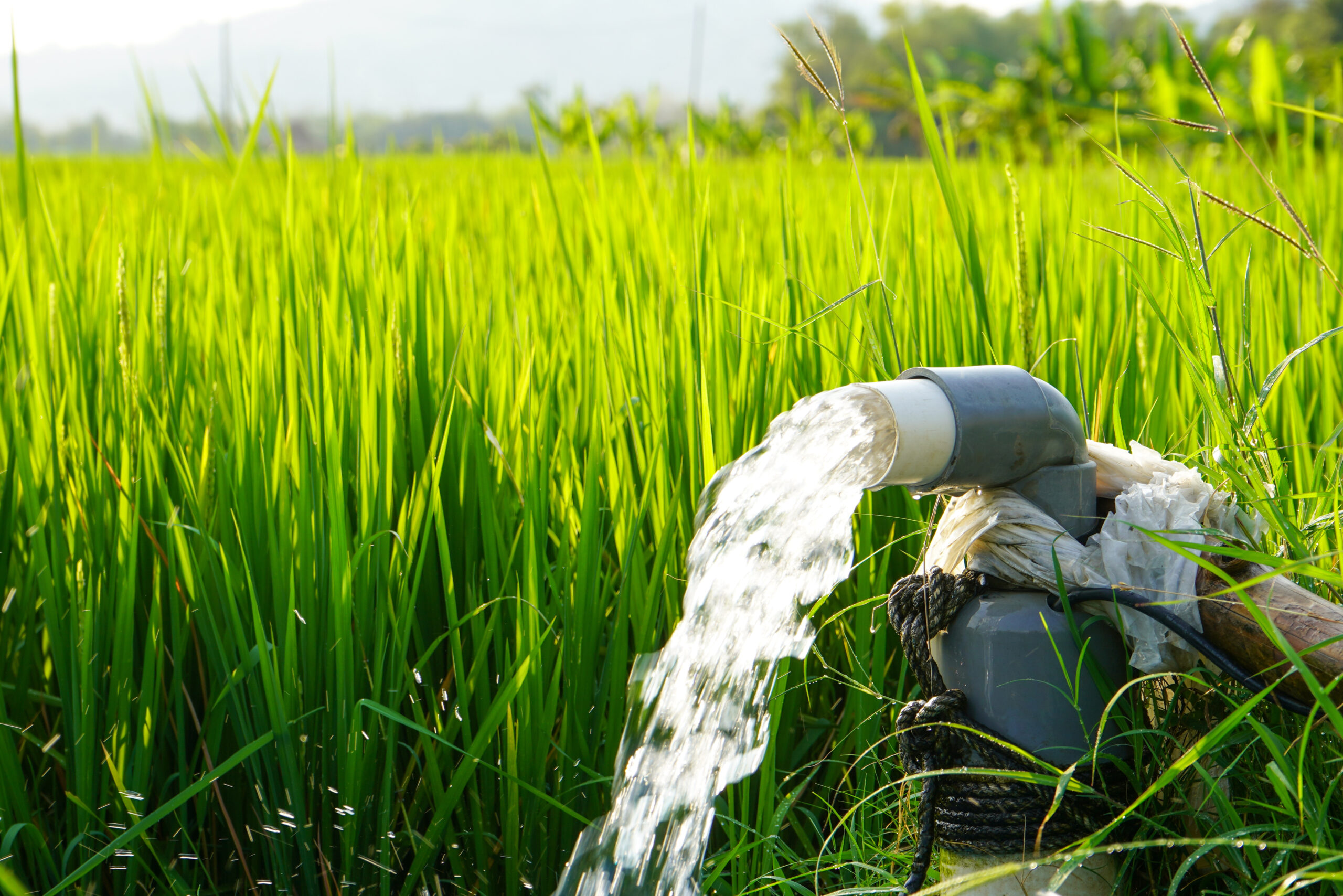
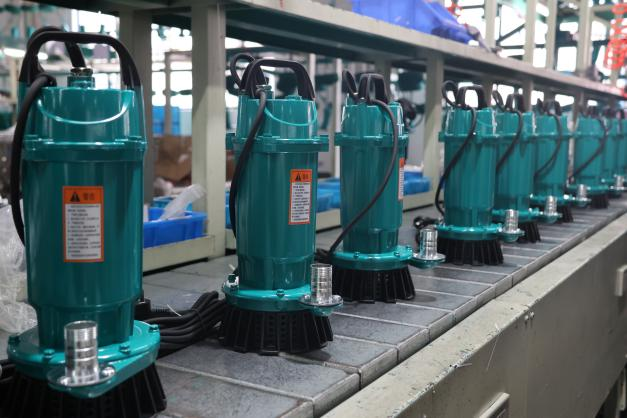
Do you know how many types of pumps and what the difference between them is? There, you can find the answer. If you don’t have a very clear understanding of water pumps, starting with the types can effectively help you.
Introduction
Water pumps, as an important machine in water treatment systems, are widely applied in many areas. Water pumps integrate pumping, delivery, and pressurization, making water usage simpler.
Choosing the wrong type of water pump can easily prevent it from functioning properly and may even cause accidents. A brief understanding of the different types of water pumps can largely prevent these problems.
Main classification methods of water pumps
Water pumps can be classified in different ways, and these different classification methods help us understand the structure or application of water pumps from different perspectives.
Below are some main classification methods.
Working principle:
Classifying by working principle is the most basic classification method, based on how the water pump transports liquid.
- Centrifugal pump: Using centrifugal force generated by the high-speed rotation to transport liquid.
- Positive displacement pump: Through the expansion and contraction chamber, the liquid is squeezed.
- Jet pump: Drawing water by generating negative pressure through a high-speed jet from the nozzle.
Installation method
According to the water pump’s installation location and structural design.
- Submersible pump: The whole water pump operates while submerged in water.
- Surface pump: Installed on the ground or above the water surface.
- Vertical/Horizontal pump: Classification based on the placement direction of the pump body.
Purpose:
The categorization method best suits your needs, helping you quickly select the type of water pump you require.
- Deep well pump: Used for pumping water from deep wells.
- Sewage pump: Designed for wastewater containing solid impurities.
- Drainage pump: For the discharge of clean water or lightly impure water.
- Booster pump: Specifically designed to increase pipeline pressure.
- Solar pump: Using solar energy for pumping water.
- Engine pump: Powered by gasoline or diesel engines.
Transport medium
Classified by the liquid medium that can be transported.
- Clean water pump: Use for conveying clean or low-impurity liquids.
- Sewage Pump/Slurry pump: Suitable for particulate, high-viscosity, or mixed liquids.
- Chemical pump: Made of corrosion-resistant materials
- Hot water pump/Circulation pump: Has a high-temperature resistant structure and can withstand the transport of hot water.
Driving method
- Electric pump: Uses electricity to drive the water pump.
- Diesel/Gasoline pump: Relies on diesel or gasoline to start the water pump.
- Solar pump: Converts solar energy into electricity to drive the water pump.
Detailed Guide to Different Types of Water Pumps
Learning different types of pumps helps you build a simple frame to quickly locate the water pumps that meet your needs. You can learn about different types of water pumps, as well as their main characteristics and applications.
Submersible Pump
A submersible pump is a type of pump totally immersed in water, usually applied in deep wells, ponds, and water towers for pumping. This pump can discharge water directly from the water source without other self-priming equipment.
- Advantages:
- Submersible pumps are put into water, which saves a lot of installation space.
2 . Under the water, it greatly reduces the noise when pumps operate.
- Thus, the compact structure makes submersible pumps easy to install and maintain.
- Applications:
- A submersible pump can be used in deep wells and boreholes to extract groundwater due to its high head.
- With a large flow rate, submersible pumps can be paired with water towers to maintain a stable water supply for agricultural irrigation.
3 . The submersible pumps can also provide domestic water for residential areas and rural communities.
Booster Pump
The booster pump is designed specifically for pressurization and is typically used in low-pressure environments or where it is required for pressurization. Ensure sufficient water flow in homes or buildings.
- Advantages:
1 . With a special design, booster pumps can increase water pressure quickly.
- When using a booster pump, it’s energy-efficient and quiet, making it ideal for residential use.
- Booster pumps can compensate for pressure in pipelines, solving the problems caused by insufficient pressure.
- Applications:
- Booster pumps can boost the pressure of household appliances, solving various problems caused by low pressure.
- A booster pump can stabilize the pressure and adjust the water pressure to supply more water to small buildings that use water simultaneously.
- Suitable for environments with continuous and frequent water demand, such as hotels, guesthouses, and apartments, ensuring stable water pressure.
Jet Pump
A jet pump utilizes high-speed water flow to create negative pressure for suctioning water. It can be drawn from low-lying water sources.
- Advantages:
- The jet pump has a strong self-priming ability; it can discharge water automatically without water intake.
- A jet pump can deal with less gravel and mud, and is less prone to clogging than other water pumps. suitable for various environments.
- Jet pumps have a higher head, making them suitable for long-distance and higher water transport or supplying water.
- Applications:
- A jet pump pumps well water from the ground directly, which is suitable for narrow deep wells or confined spaces.
- For small-scale irrigation in farmland, orchards, etc., jet pumps are highly compatible with sprinkler systems to achieve irrigation.
- Suitable for water tanks, reservoirs, and other small pumping water towers.
Centrifugal Pump
A centrifugal pump uses centrifugal force generated by the rotation of the impeller to achieve water intake and discharge. It is the most widely used pump type in many water supply systems.
- Advantages:
- The centrifugal pump’s structure is simple and has a low failure rate.
- It can provide large flow rates from tens to hundreds of cubic meters per hour and stable operation.
- Its applications range from household water use to urban water supply, which is very extensive.
- Applications:
- Stable water output and low noise make centrifugal pumps more suitable for domestic water supply.
- Suitable for factory production and industrial water use, with stable delivery and lower energy consumption for agricultural irrigation.
3 . Easy to install and portable, enabling them to meet agricultural irrigation needs.
Multi-Stage Pump
A multi-stage pump consists of multiple impellers connected in series, with each impeller increasing the pressure. The internal structure is well optimized, resulting in high efficiency.
- Advantages:
- Consisting of impellers,multi-stage pumps can easily achieve high head and long-distance transportation.
- Multi-stage pump operating efficiency is much higher than single-stage pump, saving energy and cost.
- Unique structural design makes multi-stage pumps easy to install or disassemble.
- Applications:
- Multistage pumps are highly adaptable to high pressure and high temperature, and can be used in industrial water applications.
2 . With their high head and stable pressure output, Multistage pumps can provide long-distance transportation for agricultural irrigation.
- Multistage pumps, capable of providing ultra-high pressure instantly, are also commonly used in fire protection systems.
Inline Pump
Inline pumps’ inlet and outlet with the same diameter and are on the same axis, like a pipeline. And the inline pump can be installed directly in the pipeline.
- Advantages:
- The inlet and outlet are on the same horizontal line, and the connection is easy.
2 . Small footprint, which is suitable for a narrow space.
- No additional base or alignment is required; sewage pumps can be installed faster.
- Applications:
1.It can handle both hot and cold water and is used in air conditioning and HVAC systems, making it one of the most widely used applications of inline pumps.
- In industrial applications, it can be used for heat dissipation, cleaning, and water supply of industrial machinery and equipment.
3 . Building drainage systems, such as those used in residential buildings and hotels, are designed to ensure stable water pressure on each floor.
Sewage Pump
Sewage pumps can treat liquid containing solid particles or impurities. Equipped with a strong ability to prevent blockage or wear.
- Advantages:
- Sewage pump has a large channel, a stronger impeller, and an anti-clogging design, enabling it to stably discharge types of sewage and wastewater.
- Most sewage pumps are submersible type, operate totally immersed in water, and are easy to install.
3 . Sewage pumps can adapt well to harsh environments and have high corrosion and wear resistance.
- Applications:
1 . Treating various types of domestic sewage in households or small settings.
2 . Often used to treat sewage and wastewater discharged from factories in industry.
- Sewage pumps can handle rainwater and the leaves, silt, garbage, etc., that they carry.
Solar Pump
Solar pumps using solar energy engage pumps to operate, transforming solar energy into electricity. Helping solve the water problem in areas with scarce electricity but abundant sunshine.
- Advantages:
- Solar pumps can operate without a power supply, saving energy and protecting the environment.
2 . Suitable for remote areas with no electricity or unstable power supply.
3 . Using solar power results in significant long-term savings on electricity or diesel costs.
- Applications:
- Solar pumps are applied in agriculture and animal husbandry; they can operate for
a long time.
- Solar pumps are very suitable for remote engineering projects.
- Solar pumps can also be used by rural households to draw water from deep wells, ponds, etc.
Gasoline / Diesel Pump
Gasoline /Diesel pumps use a diesel or gasoline engine as their power source to operate. They don’t require electricity, so they can pump anytime, anywhere.
- Advantages:
1.No power required, extremely mobile. It can operate in the absence of electricity.
2 . Easy to move and quick start, suitable for emergencies.
- High traffic volume and high efficiency.
- Applications:
1.Gasoline /Diesel pump suitable for farmland without electricity or mobile irrigation.
- High-flow gasoline pumps are the most common equipment at flood control sites, capable of flood control and efficient emergency pumping.
- Both gasoline and diesel pumps are very suitable for field operations or areas without electricity, such as forest areas and border defense.
Conclusion
Different kinds of water pumps have their own strengths, whether in structure, performance, or where they’re used. For example, solar pumps and diesel pumps are suitable for situations without electricity. The type of water pump affects the pump’s performance, system efficiency, pump lifespan, and maintenance costs. If you are unsure about the type of water pump you need, please consult a professional water pump supplier and manufacturer, HunGerät. We will help you find the most suitable water pump based on your needs.
FAQ
Q1:What head of pump is needed for pumping water from a household well?
A1: The head depends on the depth of the water source. Commonly, the shallow wells can choose a head of about 10-15m, for the deep well, 20m is better. If the head is too low, the water pressure will be small or hard to discharge.
Q2: Can a Sewage pump be used to pump domestic sewage?
A2: Yes, a Sewage pump is specialized for transporting liquid containing solid particles and impurities. But for large solids or fibers, choosing models with strong anti-clogging capabilities is better.
Q3: Can a Solar Pump operate for a whole day?
A3: The solar pump operates depending on sunlight. Thus, it can operate normally during sunny days. When it is cloudy or at night, solar pumps require power lines to maintain operation and ensure a continuous water supply.
Q4: What is the difference between a booster pump and a jet pump?
A4: The Booster pump is mainly used to increase the water pressure, but it has no self-priming function. A jet pump can be self-priming to discharge water from low places.